![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Updated in
Updated in
![]() 2025 :
2025 :
![]() 9 :
9 :
![]() 9 (Tuesday) :
;
9 (Tuesday) :
;
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Updated on
Updated on
9 :
9 :
2025 :
 Pipelining ;
Pipelining ;
。
| 2 | 1 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 3 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 2 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
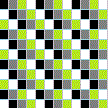
9 | x | 9 | , | a | . | k | . | a | . |
|
Sudoku | |||||||||||||
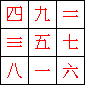 |
Lo | Shu | Magic | Square | i | . | e | . | numerological | ( | 6 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
Magic | Square | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 3 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
(![]() IC28,
IC28,
IC16,
IC1,
![]() ICC), also see:
Algorithm; Network
Topology;
Pipelining;
ICC), also see:
Algorithm; Network
Topology;
Pipelining;
 doko
doko ![]() WHERE ({FF,CC,99}, {FF,CC,88}) are on the defined ZCS ... ; Remark: since 2025,
(Display, screen, Walls) may become arch alike (in addition to lines) because of
PCS based computing has begun in addition to ZCS based computing;
WHERE ({FF,CC,99}, {FF,CC,88}) are on the defined ZCS ... ; Remark: since 2025,
(Display, screen, Walls) may become arch alike (in addition to lines) because of
PCS based computing has begun in addition to ZCS based computing;
I wrote: in
numerological,
![]() ware ware We've only (9, 0) i.e.
ware ware We've only (9, 0) i.e.
![]() aesthetics, similar to (TRUE, FALSE),
aesthetics, similar to (TRUE, FALSE), ![]() And Then, "9" in
And Then, "9" in
![]() deduction would be (3, 6,
9),
deduction would be (3, 6,
9), ![]() And Then, (non (Val, Ref) are
Numelological0) alike,
And Then, (non (Val, Ref) are
Numelological0) alike, ![]() And Then, Number ... ; Also see:
And Then, Number ... ; Also see:
![]() philosophy;
philosophy;
well trained kids!! replied: HOW About Hex sir?
I wrote: Remark: 2003 design
model executable application (Pre School English
Typing) is still very useful ... ; try to realize & understand
Numerical values in
numerology, e.g. ![]() WHICH (English, EN language code (letter,
LETTER))
belongs to ... ;
WHICH (English, EN language code (letter,
LETTER))
belongs to ... ;
I wrote: since
2017,  Origin of Sound has been defined, and I need to QA only
ACT2 and
ACT3
level imaginary hyperspace R&D related kids, so quiz would be: HOW would you
like to fill the iroLED (
Origin of Sound has been defined, and I need to QA only
ACT2 and
ACT3
level imaginary hyperspace R&D related kids, so quiz would be: HOW would you
like to fill the iroLED (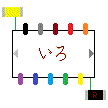 iroColourWaveForm) colors inside of the above table between Green (3,3,3) and
Blue (3,3,3)?
iroColourWaveForm) colors inside of the above table between Green (3,3,3) and
Blue (3,3,3)?
well trained kids!! replied: Umm!! Hmm!! Yellow Color (Cell (s)) sir;
I wrote: (![]() mochiron,
mochiron,
![]() mochiron,
mochiron,
![]() mochiron,
mochiron,
![]() mochiron Of Course) : (of
course,
certainly,
naturally);
mochiron
mochiron Of Course) : (of
course,
certainly,
naturally);
mochiron
![]() of course; You can
have your "Origin of Sound" patterns ... and be beyond Yellowish Variation (Y V)
ZCS based computing ... ;
of course; You can
have your "Origin of Sound" patterns ... and be beyond Yellowish Variation (Y V)
ZCS based computing ... ;
。
|
I wrote: don't forget THAT 45
degree to "Pipelining" is called "parallel computing" ; Also see:
Cloud Computing, doko
![]() WHERE
Keywords
are characteristics via words ... e.g. (AC,
DC),
(BE,
FE),
(LM,
VM),
... ;
WHERE
Keywords
are characteristics via words ... e.g. (AC,
DC),
(BE,
FE),
(LM,
VM),
... ;
well trained kids! replied: we've already learnt THAT "Pipelining Computing" has been since 1980s, if compare to "Cloud Computing" has been since 2000, and Idea Processor based computing is NOT officially yet as of 2020s, and can you please teach us HOW Idea Processor Computing sir ?
I wrote:
Idea Processor is
beyond GPS, and do you realize and understand 2 (1 mm ones) gravity spots are
embedded As Device
1st; prior to GPS was
Translator and to be able to do translation (multiple Language Codes), we've to
define good words in Dictionary As Index
2nd;
![]() And Then, Calculator, Dictionary, Translator, GPS, ... As
And Then, Calculator, Dictionary, Translator, GPS, ... As
![]() Induction Logic (also see:
philosophy)
3rd;
Induction Logic (also see:
philosophy)
3rd;
I've a quiz i.e. HOW will you design and model GDC (Gravity Dimension Computer) ? WHAT kind of tools would you like to use ?
well trained kids! replied:
we'll be using iroLED, Optics, Sizes of Gravity Spot,
surfaces
(![]() NCS,
NCS,
![]() PCS,
PCS,
![]() ZCS), ... sir ;
ZCS), ... sir ;
I wrote:
mochiron
![]() of course;
of course;
A basic Time-oriented instruction-fetching pipelining-method is shown; but, there are many other ways of methods such as Pipe-oriented, Frequency-oriented, Material-oriented, and ...; Pipelining enhances more throughput gain, and faster processing speed gain; Notice the 2 dimensional Time/Pipe pipelining. SiO2 based technology limits 2 dimensions only. Optical computing (also see: Optics) in the future will compute more than 2 dimensions. In traditional SiO2 based technology, even though numbers of pipes can be increased to achieve more throughput gain, but more numbers of pipes make very difficult human un-understandable complexity to code. Also see: Driver-to-load ratio;
For systems experts only: before developing optical computing, calculate through put gain in Time/Pipe while multitasking; where through put gain = more numbers of executed tasks ;
Time1 Time2 Time3 Time4 Time5 Time6 Time7 Time8 TimeN-1 Time N
Pipe #1: Task1 Task1
Pipe #1: Task0 Task0 Task2 Task2 Task2 Task4 Task4
Pipe #2: Task2 Task2 Task2 Task2 Task2 Task2 Task2
Pipe #3: Task3 Task3 Task3
Pipe #3: Task0 Task0 Task0 Task4 Task4 Task4 Task4
Pipe #4: Task4 Task4 Task4 Task4 Task4 Task4 Task4 Task4
Pipe #5: Task5 Task5 Task5 Task5
Pipe #5: Task0 Task0 Task0 Task0 Task6 Task6
Pipe #6: Task6 Task6 Task6 Task6 Task6 Task6
TaskN-1
Task N
point-to-point; Point to point; e.g.
![]() point-to-point;
point-to-point;
![]() point-to-point;
point-to-point;
![]() point-to-point;
point-to-point;
![]() point-to-point;
point-to-point;
![]() pointokarapointoe Point-to-point; Also see:
IoT;
Physics Law 198;
Pipelining;
Protocol and Port;
Router;
pointokarapointoe Point-to-point; Also see:
IoT;
Physics Law 198;
Pipelining;
Protocol and Port;
Router;
舰㠂आ蘪虈܁ꀂʂ〩ʂȥā1ରआ蘪虈܁ꀁʂ 」ʂ〉Ƃꁶȃ ȁဂꛑё栻꼍Ꝍ軐퓱ꅹरԆหȃԝㄘ〖ؔ唃ഓ摁業楮瑳慲潴ひᜠ」〹ㄲ㐷〱娲༘ㄲ㤰㜱㜱ㄴ㈰ずㄘ〖ؔ唃̄ഓ摁業楮瑳慲潴ひ龁ര आ蘪虈āԁ̀趁要脂沥ꀟ☟贊囇囬乿넵髇쯶㨃麙蛸蔜솙踠㰳㾡⊦潎쯮O밍ギ怆啸푍黟䔂揀䋉織녙ꦂ䨘氶��띍謄ᅍ埭ꅭ擺혛��臨缸᠏��偏熂ഥ䂮♯紏ࡷ袝ᔢⓄ姠攜֣̂ꌁずじؕ唃┝คర ਆ ث Ё舁Ѓ㐰ᵕБꀫة⬊Ć Ą㞂Ȕꀃఛ䄙浤湩獩牴瑡牯啀䅓奍乁䅍R र̆ᵕ Г。 ̎ᴂ 脃ꊉ煌듼ﺎ⟲捦胎ᶧ쀘䵯䪠ꮱ㵸㑠钨㖃須춹ꄆꥉ諓㽑䀰˅ꜭ貕賄㔲㿄旐츧䠔ɟ큻์癸뽣娜릫惧뼤宬桦㷒ʐ㮉섮祑ȝ㬢椖娘ᖅϩ왱㉷Ȣ1
|
|
|