![]() Updated in
Updated in
2024 :
3 :
19 :
![]() :
: ![]() :
:
![]() :
a ECG;
:
a ECG;
Remark:
![]() I'm still developing "ecg Interpretation," NOT completed ones yet;
I'm still developing "ecg Interpretation," NOT completed ones yet;
Remark: (Font Color (Maroon); Highlight (Hex (FF,FF,99))), doko WHERE ((Font Color (Hex (11,11,11)) with Highlight (Aqua))) to be defining and knowing by Gene Therapy System;
aberrancy (deviation from norms);
ablation (Method, Procedure, Technique) can cure abnormal heart (e.g. irregular heartbeats, a.k.a. arrhythmias); Also see: a G T S U;
accelerated i d i o-ventricular rhythm;
acceleration dependent block;
accessory pathway;
![]() A c e b u t o l o l, beta blocker for treating angina (chest pain), high blood
pressure, irregular heartbeat, ... ; Also see:
Bio Chemical
Physical Similarity ... ;
A c e b u t o l o l, beta blocker for treating angina (chest pain), high blood
pressure, irregular heartbeat, ... ; Also see:
Bio Chemical
Physical Similarity ... ;
Acetylcholine;
ACTION Potential (Contractile Cell, Drug Effect, Pace-marker Cell) ... ;
acute coronary syndrome, also see: Diseases...;
acute myocardial infarction;
Adenosine;
(![]() AF,
AF, ![]() AF,
AF,
![]() AF)
Atrial Fibrillation,
chaos conditions of atria, characterized by the absence of P waves on the ECG;
Remark:
atria generates (350 - 600) impulses / min; AV node is overwhelmed with atrial
impulses;
AF)
Atrial Fibrillation,
chaos conditions of atria, characterized by the absence of P waves on the ECG;
Remark:
atria generates (350 - 600) impulses / min; AV node is overwhelmed with atrial
impulses;
ambulatory ECG monitoring;
A m i o d a r o n e;
![]() A m l o d i p i n e, Calcium channel blocker for treating angina
(chest pain), high blood pressure, ... ; Also see:
Bio Chemical
Physical Similarity ... ;
A m l o d i p i n e, Calcium channel blocker for treating angina
(chest pain), high blood pressure, ... ; Also see:
Bio Chemical
Physical Similarity ... ;
a m p l i t u e;
Angioplasty, a.k.a. balloon angioplasty, a.k.a. percutaneous trans luminal angioplasty; in common, Tx (arterial atherosclerosis), an endovascular procedure to widen (arteries, vein) because (narrowed (arteries, vein), obstructed (arteries, vein)) is abnormal;
anemia;
anterior myocardial infraction;
anti-arrhythmic;
antifungal;
aortic steno sis;
aortic valve;
apical ballooning syndrome, also see: Disease...;
arrhythmia;
a r r h y t h m o g e n i c right ventricular cardio-myopathy;
artifact;
Ashman phenomenon;
atherosclerosis, arteries' disease (e.g. deposition of fatty plaques material at the inner walls); Also see: p ECG (angioplasty) ... ;
(![]() Atria,
Atria, ![]() Atria,
Atria,
![]() Atria) : atria is plural
noun usage if compare to singular usage "atrium", e.g. 2 atria are chambers
receiving blood from the veins; atria (thin Walls), if compare to ventricular
(thick Walls) e.g. 2 ventricles are chambers (pumping, sending) blood out of the
heart;
Atria) : atria is plural
noun usage if compare to singular usage "atrium", e.g. 2 atria are chambers
receiving blood from the veins; atria (thin Walls), if compare to ventricular
(thick Walls) e.g. 2 ventricles are chambers (pumping, sending) blood out of the
heart;
atria (2 upper cavities of the heart) pass blood to ventricles;
left,
e.g.
left atrium receives
oxygenated blood from the pulmonary vein;
right,
e.g.
right atrium receives
deoxygenated blood from the veins of the body;
atrial (Atrial Conduction System, Atrial Enlargement, Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Atrial Foci);
Atrioventricular re-entry tachycardia;
atypical chest pain;
augmented lead;
automated external defibrillator;
automatic it y;
autonomic nervous system;
(![]() AV,
AV,
![]() AV,
AV,
![]() AV) e.g. (AV Block, AV
Dissociation, AV junction ablation, AV nodal re-entry tachycardia); Also see:
Atrioventricular;
AV) e.g. (AV Block, AV
Dissociation, AV junction ablation, AV nodal re-entry tachycardia); Also see:
Atrioventricular;
(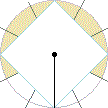 a V F,
a V F,
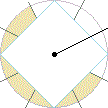 a V L,
a V L,
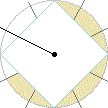 a V R), also see:
Hexaxial
Reference System;
a V R), also see:
Hexaxial
Reference System;
axis e.g. (Axis, Axis Deviation, Axis Causes);
s h i n b o Atrial;
Sport Medicine e.g. athlete's ECG;
(![]() e c g Interpretation,
e c g Interpretation,
![]() e c g
Interpretation,
e c g
Interpretation,
![]() e c g
Interpretation), also see:
ecg Interpretation;
e c g
Interpretation), also see:
ecg Interpretation;
|
|
|
|
|
|